Using what you have learned about carbon bonds and energy in this lesson what can you say about the amount of carbon bonds in this food component Carbon in the Atmosphere. mc026-1.jpg. By how much did carbon dioxide levels increase from 1980 to 2000? What is stored in carbon bonds?Carbon and its bonds are key to understanding chemistry. Here is an overview of the most common type of bond and a few others. For example, the bond between calcium and carbon in calcium carbide, CaC2, is an ionic bond. Calcium and carbon have different electronegativities from each other.In carbon bonding, the carbon atoms link with each other to form a straight chain, branched chain, and different types of rings. Carbon-Carbon double bonds in ethane molecule: Double bond between two carbon atoms and single bonds between carbon and hydrogen are shown in the figure...What is a carbon-carbon bond? You might think this is a question with a simple answer, but chemists are still working to figure it out. To do so, they are Lines and arrows drawn on a page to show electron movement between atoms often describe what is happening in reaction flasks pretty well.Carbon footprint and intensity analysis provides the basis for portfolio decarbonization, tilt and Green bonds and even sovereign green bonds are emerging strategies for taking advantage of the "How carbon efficient is my portfolio?" "What are the emissions per unit of sales for the portfolio companies?"
What Type of Bonds Does Carbon Form?
Dhanalakshmi. June 1, 2019, 11:43am #1. What is stored in carbon bonds?Compare the bond enthalpies of the carbon-carbon single, double, and triple bonds. Based on this information, what is the average pi-bond contribution to bond enthalpy. I know that there are 2pi and 1 sigma... I just have no idea where to go from there.Chemical compound - Chemical compound - Carbon bonding: The carbon atom is unique among elements in its tendency to form extensive networks of When fully bonded to other atoms, the four bonds of the carbon atom are directed to the corners of a tetrahedron and make angles of about...What elements does carbon bond with to make up life's molecules? Carbon-carbon bonds can be single, double, or triple covalent bonds. Chains of carbon atoms can even close up on Nucleic acids store and transmit hereditary, or genetic, information. Some proteins controle the rate of reactions...

Learn About Carbon Bonding | Chegg.com
In carbs, its mainly stored in both carbon-carbon bonds and carbon-oxygen bonds. Cellular respiration, because it releases the energy stored in carbon bonds by photosynthesis, and recombines carbon into carbon dioxide.bond line structure the carbon on the right is still bonded to three hydrogen's all right but again we leave those off when we're drawing a bond line structure let's see how many bonds we already have we'll start with the car in magenta the carbon in magenta already has one bond and a neutral carbon...Definition: What is a Chemical Bond? Chemical bonds are forces that hold the atoms together in a molecule. They are a result of strong intramolecular interactions among the atoms of a molecule. Our body uses the energy stored in chemical bonds in order to do work and keep it active and functional.varshakhatri778 varshakhatri778. Energy is stored carbon bonds. We're in the know. This site is using cookies under cookie policy. You can specify conditions of storing and accessing cookies in your browser.Bonds are issued by 3 entities: U.S. government, state and local governments and corporations. Read this article to learn more. Bonds issued by the federal government are called Treasury bonds. Backed by the full faith and credit of the United States government, Treasuries are regarded as one of...
Jump to navigation Jump to search
A carbon–carbon bond is a covalent bond between two carbon atoms.[1] The most common form is the one bond: a bond composed of 2 electrons, one from each of the two atoms. The carbon–carbon unmarried bond is a sigma bond and is shaped between one hybridized orbital from every of the carbon atoms. In ethane, the orbitals are sp3-hybridized orbitals, however unmarried bonds shaped between carbon atoms with different hybridizations do happen (e.g. sp2 to sp2). In truth, the carbon atoms in the single bond need not be of the same hybridization. Carbon atoms too can shape double bonds in compounds referred to as alkenes or triple bonds in compounds known as alkynes. A double bond is shaped with an sp2-hybridized orbital and a p-orbital that is no longer involved in the hybridization. A triple bond is shaped with an sp-hybridized orbital and two p-orbitals from each and every atom. The use of the p-orbitals forms a pi bond.
Chains and branching
Carbon is some of the few parts that can form long chains of its own atoms, a assets called catenation. This coupled with the power of the carbon–carbon bond provides upward push to a massive choice of molecular forms, lots of which can be essential structural elements of existence, so carbon compounds have their very own box of research: natural chemistry.
2,2,3-trimethylpentaneBranching is additionally common in C−C skeletons. Carbon atoms in a molecule are categorized through the choice of carbon neighbors they have got:
A Primary carbon has one carbon neighbor. A Secondary carbon has two carbon neighbors. A Tertiary carbon has three carbon neighbors. A Quaternary carbon has four carbon neighbors.In "structurally complex organic molecules", it is the three-d orientation of the carbon–carbon bonds at quaternary loci which dictates the form of the molecule.[2] Further, quaternary loci are discovered in many biologically lively small molecules, corresponding to cortisone and morphine.[2]
Synthesis
Carbon–carbon bond-forming reactions are organic reactions in which a brand new carbon–carbon bond is shaped. They are important in the production of many man-made chemical compounds akin to pharmaceuticals and plastics.
Some examples of reactions which shape carbon–carbon bonds are aldol reactions, Diels–Alder reaction, the addition of a Grignard reagent to a carbonyl staff, a Heck response, a Michael response and a Wittig response.
The directed synthesis of desired three-d constructions for tertiary carbons was once in large part solved all the way through the past due 20th century, however the same talent to direct quaternary carbon synthesis did not start to emerge till the primary decade of the twenty first century.[2]
Bond strengths and lengths
Relative to maximum bonds, a carbon–carbon bond is very strong.[3]
C–C bond Molecule Bond dissociation energy (kcal/mol) CH3−CH3 ethane 90 C6H5−CH3 toluene 102 C6H5−C6H5 biphenyl 114 CH3C(O)−CH3 acetone 84 CH3−CN acetonitrile 136 CH3−CH2OH ethanol 88The values given above constitute bond dissociation energies which might be often encountered; from time to time, outliers may deviate vastly from this range. In the highly congested hexakis(3,5-di-tert-butylphenyl)ethane, the bond dissociation power to shape the stabilized triarylmethyl radical is most effective 8 kcal/mol.[4] On the other extreme, the central carbon–carbon single bond of diacetylene is very sturdy at A hundred and sixty kcal/mol, as the one bond joins two carbons of sp hybridization.[5] Carbon–carbon more than one bonds are generally more potent; the double bond of ethylene and triple bond of acetylene were determined to have bond dissociation energies of 174 and 230 kcal/mol, respectively.[6]
A standard carbon–carbon single bond has a length of 154 pm, while a standard double bond and triple bond are 134 pm and A hundred and twenty pm, respectively. Also a outcome of its severe steric congestion, hexakis(3,5-di-tert-butylphenyl)ethane has a very much elongated central bond with a duration of 167 pm. On the opposite hand, an overly quick triple bond of One hundred fifteen pm has been seen for the iodonium species [HC≡C–I+Ph][CF3SO3–], because of the strongly electron-withdrawing iodonium moiety.[7]
Comparison of bond lengths in easy hydrocarbons[8] Molecule Ethane Ethylene Acetylene Formula C2H6 C2H4 C2H2 Class alkane alkene alkyne Structure Hybridisation of carbon sp3 sp2 sp C-C bond period 1.535 Å 1.339 Å 1.203 Å Proportion of C-C single bond 100% 87% 78% Structure choice means microwave spectroscopy microwave spectroscopy infrared spectroscopySee also
Carbon–hydrogen bondReferences
^ .mw-parser-output cite.citationfont-style:inherit.mw-parser-output .quotation qquotes:"\"""\"""'""'".mw-parser-output .id-lock-free a,.mw-parser-output .quotation .cs1-lock-free abackground:linear-gradient(clear,transparent),url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/6/65/Lock-green.svg")correct 0.1em heart/9px no-repeat.mw-parser-output .id-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .id-lock-registration a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .quotation .cs1-lock-registration abackground:linear-gradient(transparent,transparent),url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg")appropriate 0.1em heart/9px no-repeat.mw-parser-output .id-lock-subscription a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription abackground:linear-gradient(clear,clear),url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg")correct 0.1em center/9px no-repeat.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registrationcolor:#555.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration spanborder-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:lend a hand.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon abackground:linear-gradient(transparent,transparent),url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg")appropriate 0.1em heart/12px no-repeat.mw-parser-output code.cs1-codecolour:inherit;background:inherit;border:none;padding:inherit.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-errordisplay:none;font-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-errorfont-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-maintdisplay:none;colour:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em.mw-parser-output .cs1-formatfont-size:95%.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-leftpadding-left:0.2em.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-rightpadding-right:0.2em.mw-parser-output .citation .mw-selflinkfont-weight:inheritDembicki, Harry (2016-10-06). Practical Petroleum Geochemistry for Exploration and Production. Elsevier. p. 7. ISBN 9780128033517. ^ a b c Quasdorf, Kyle W.; Overman, Larry E. (2014). "Review: Catalytic enantioselective synthesis of quaternary carbon stereocentres". Nature (paper). 516 (7530): 181–191. Bibcode:2014Natur.516..181Q. doi:10.1038/nature14007. PMC 4697831. PMID 25503231. ^ Yu-Ran Luo and Jin-Pei Cheng "Bond Dissociation Energies" in CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 96th Edition. ^ Rösel, Sören; Balestrieri, Ciro; Schreiner, Peter R. (2017). "Sizing the role of London dispersion in the dissociation of all-meta tert-butyl hexaphenylethane". Chemical Science. 8 (1): 405–410. doi:10.1039/c6sc02727j. ISSN 2041-6520. PMC 5365070. PMID 28451185. ^ "NIST Webbook". ^ Blanksby, Stephen J.; Ellison, G. Barney (April 2003). "Bond Dissociation Energies of Organic Molecules". Accounts of Chemical Research. 36 (4): 255–263. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.616.3043. doi:10.1021/ar020230d. ISSN 0001-4842. PMID 12693923. ^ 1927-, Streitwieser, Andrew (1992). Introduction to natural chemistry. Heathcock, Clayton H., 1936-, Kosower, Edward M. (4th ed.). Upper Saddle River, N.J.: Prentice Hall. p. 574. ISBN 978-0139738500. OCLC 52836313.CS1 maint: numeric names: authors checklist (hyperlink) ^ CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 88th edition vteCompounds of carbon with other parts in the periodic desk CH He CLi CBe CB CC CN CO CF Ne CNa CMg CAl CSi CP CS CCl CAr CK CCa CSc CTi CV CCr CMn CFe CCo CNi CCu CZn CGa CGe CAs CSe CBr CKr CRb CSr CY CZr CNb CMo CTc CRu CRh CPd CAg CCd CIn CSn CSb CTe CI CXe CCs CBa CLu CHf CTa CW CRe COs CIr CPt CAu CHg CTl CPb CBi CPo CAt Rn Fr CRa Lr Rf Db CSg Bh Hs Mt Ds Rg Cn Nh Fl Mc Lv Ts Og CLa CCe CPr CNd CPm CSm CEu CGd CTb CDy CHo CEr CTm CYb Ac CTh CPa CU CNp CPu CAm CCm CBk CCf CEs Fm Md No LegendChemical bonds to carbonCore natural chemistryMany uses in chemistryAcademic research, no standard useBond unknown Retrieved from "https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Carbon–carbon_bond&oldid=1015457561"Scientists created fuel through artificial photosynthesis ...

Cytoplasmic Organelles

Organic Chemistry General organic chemistry 5 The total ...

VI. Compounds with Carbon-Hydrogen Bonds - Chemistry ...

Adenosine Triphosphate - Assignment Point

The Carb-Sane Asylum: A Fein(man), Fine Mess of Thermodynamics

science in a can, ATP: The energy of the cell The endgame ...

Challenges in the use of hydrogen for maritime ...

Daily Challenges | Brilliant

PPT - Chapter 9 Alkynes PowerPoint Presentation, free ...

Chemical energy is stored in the bonds of carbohydrate ...

Comparing Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration

Obtaining and Transforming Energy: Role of ATP - Expii

ATP and Sources of Energy.pptx on emaze

Chemical Energy PE stored in chemical bonds KE energy of ...

Coupling Through Emergent Conservation Laws (Part 3) | Azimuth
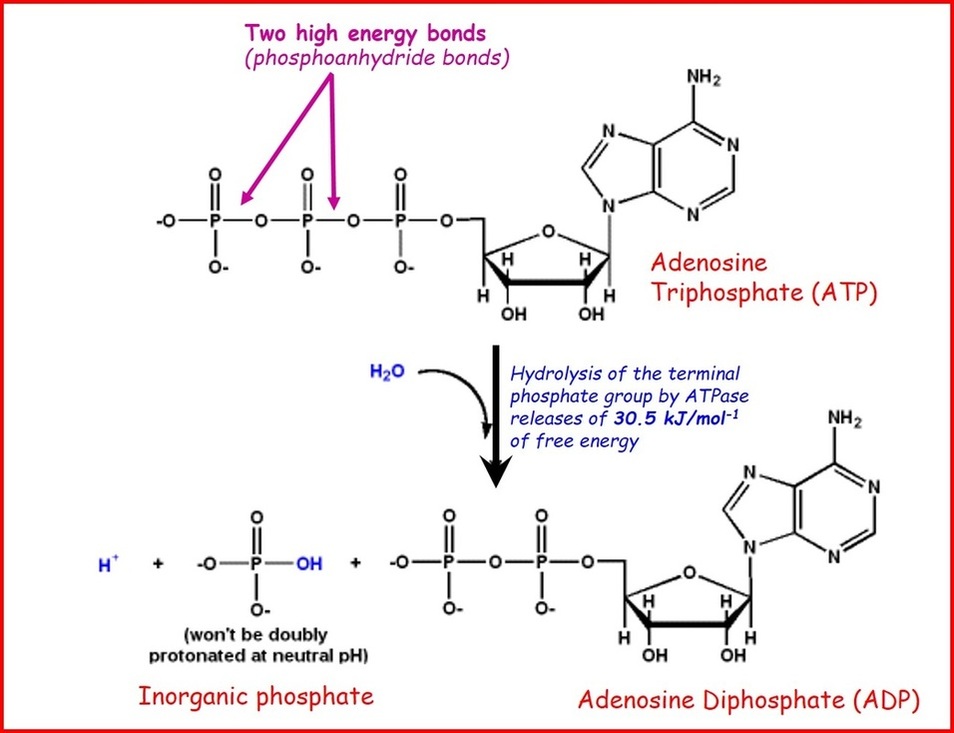
ATP and Sources of Energy.pptx on emaze

PPT - 1. What kind of energy is stored in bonds of ...

CARBOHYDRATES -Biochemistry - BioChemiThon

PPT - Organic Molecules - The Building Blocks of Life ...

What Do Chloroplasts Use to Make Glucose? | Sciencing

0 comments:
Post a Comment